December 15th, 2020
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE IONS: RISKS AND BENEFITS
understanding water / water as a remedy / property 01: ionization
Positive ions: the risks
In recent times the already excessive concentration of positive ions has been subject to a further increase. This phenomenon has mainly been caused by the technological advance of human society and, since the atmospheric contamination destroys the negative ions that are there, it concerns every city.
It is believed that an excessive positive ionization of the air could be dangerous for both human beings, animals and plants. Some studies identify as its most common repercussions weariness, headaches, asphyxiation, allergies, a tendency to depression, nervousness and insomnia.
It is also remarked that every electrical device in our houses produces as much positive ions as our bodies.
It is true that negative ions catch positive ions and neutralize them; at the same time, though, given the overwhelming number of positive ions we are plunged in, this looks like an unfair battle.
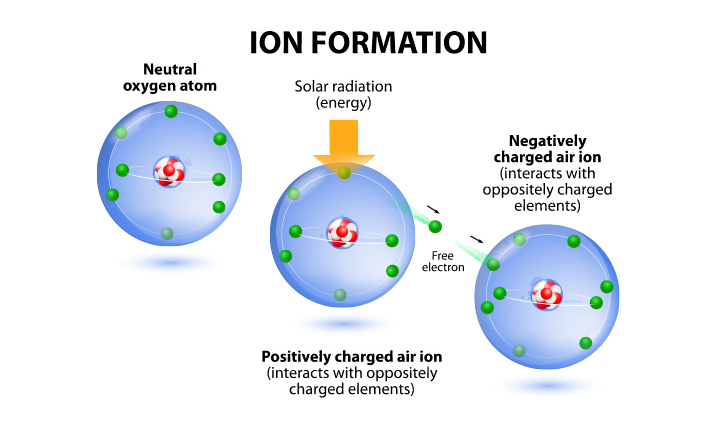
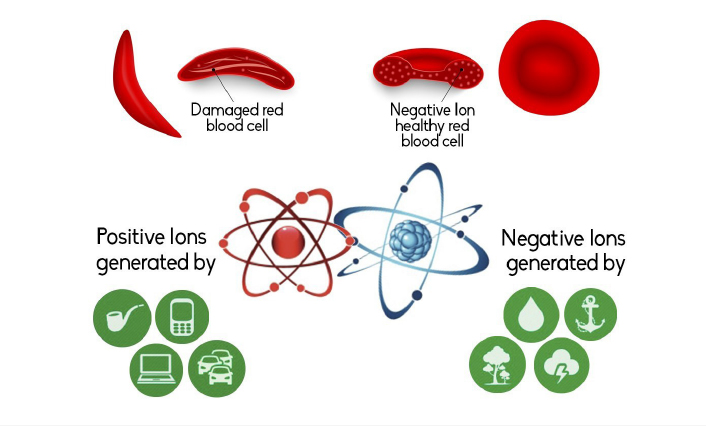
↑ Ions formation, origins and consequences
Negative ions: the benefits
Bodies need negative ions, which contribute to the regulation of human metabolism.
The problem is that, notwithstanding the abundance of negative ions in nature, practically everything we do creates positive ions and the closer we get to cities, the fewer negative ions are available. Inside our houses there are even fewer.
It seems that negative ions regulate the levels of serotonin (responsible for our good mood), have a sedative effect and, as we saw before, make the air we breathe in cleaner.

↑ Negative ions can contribute to our psycho-physical balance

↑ Negative ions are naturally created by the shower
It’s worth considering that only negatively ionized oxygen can penetrate though the membrane of our lungs and be absorbed by blood, making it simpler to remove the carbon dioxide from the blood in our veins as a by-product of breathing.
Nonetheless such process underlies the inhalation of ‘small ions’ which cannot be produced by most common ionization machines.
In this sense, showers could offer a good contribution to the extent that they naturally create negative ions; keeping them active all day long wouldn’t, though, be neither practical or convenient.
To fix this, though, we can adopt a different view and enjoy storms, which are one of the sources; take a summer stroll in the mountains, where negative ions are naturally present in a greater concentration; experiment with the splashes of a waterfall such as the one in Paley Park when it’s possible.
Negative ions purify air
An important feature of the air around us is its ionization: almost all the particles that are suspended in it have a positive charge, but the opposite happens for negative ions. Negative ions and particles are therefore magnetically and reciprocally attracted, making negative ions the most powerful natural air purifiers.
There isn’t, in fact, anything so effective as negative ions to catch allergens and contaminants from the air we breathe.
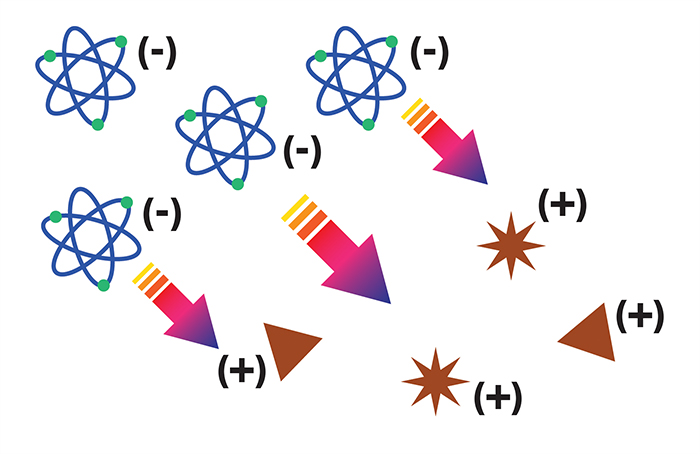
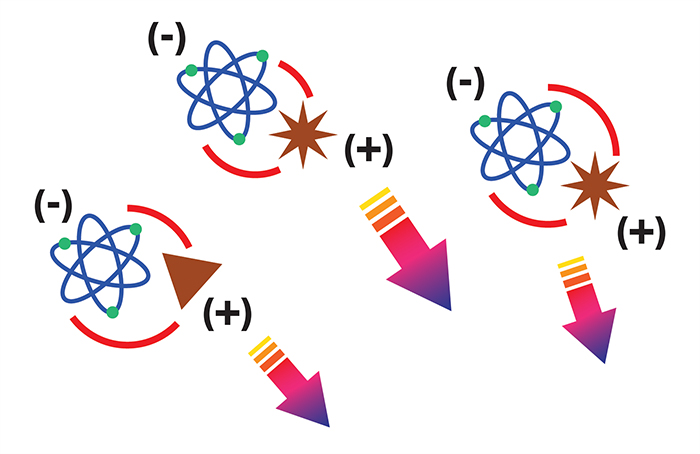
↑ How negative ions purify the air