January 30th, 2021
PARTICULATE: PM, PM10, PM2.5
sustainability / water as a remedy
Particulate is the pollutant with the highest environmental impact in urban areas and it is constituted by dust, smoke and droplets which, due to their relatively small size, disperse in the air. In technical jargon, it is called aerosol.
It is estimated that 10 million tons of particulate are introduced in the air every day, 94% of them coming from natural sources. Their long persistence in the atmosphere is caused by the size of such particles, alongside with the nature of winds and waterfalls.
As far as terminology is concerned, the total suspended dust or TSP is also referred to with the term PM – Particulate Matter. The acronym PM10, on the other hand, identifies one of the many fractions by which particulate is classified, as it is found in the atmosphere in particles with an aerodynamic diameter equal or lower than 10 microns.
About 60% of PM10 is made up of smaller particles which are in turn named PM2,5, capable of reaching the air sacs in our lungs in 30 days.
We also need to remember that PM10 can remain in suspension for 12 hours, while PM1 can fluctuate for as long as a month.
→ Particulate matter is the sum of all solid and liquid particles suspended in air

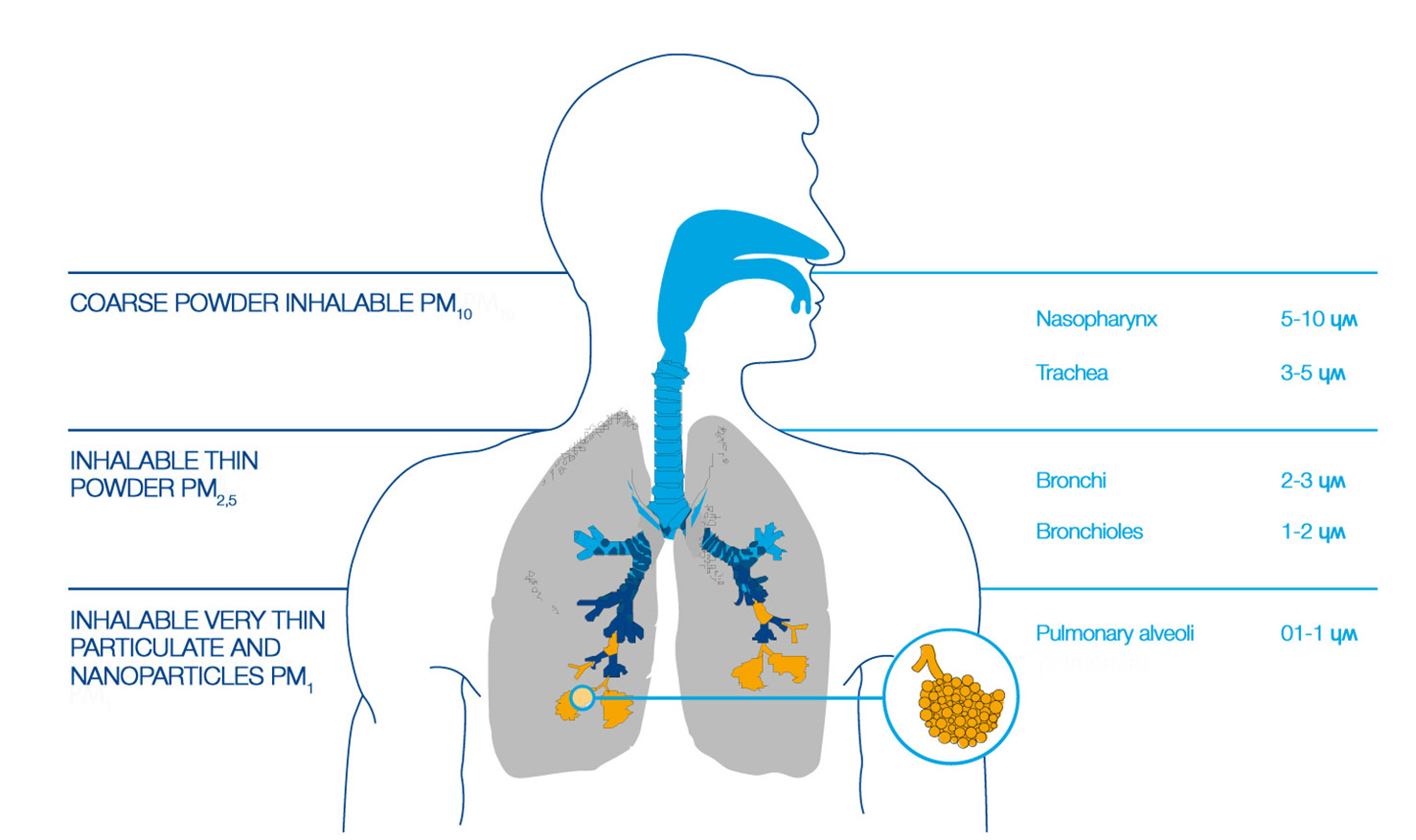
↑ Particulate matter and lung health
Sources
Particulate matter mainly originates from combustion (primary particulate matter, that is produced directly) and as a by-product of gas reactions (secondary particulate matter). The rough fraction of particulate generally originates from mechanical processes (primary particulate matter only).
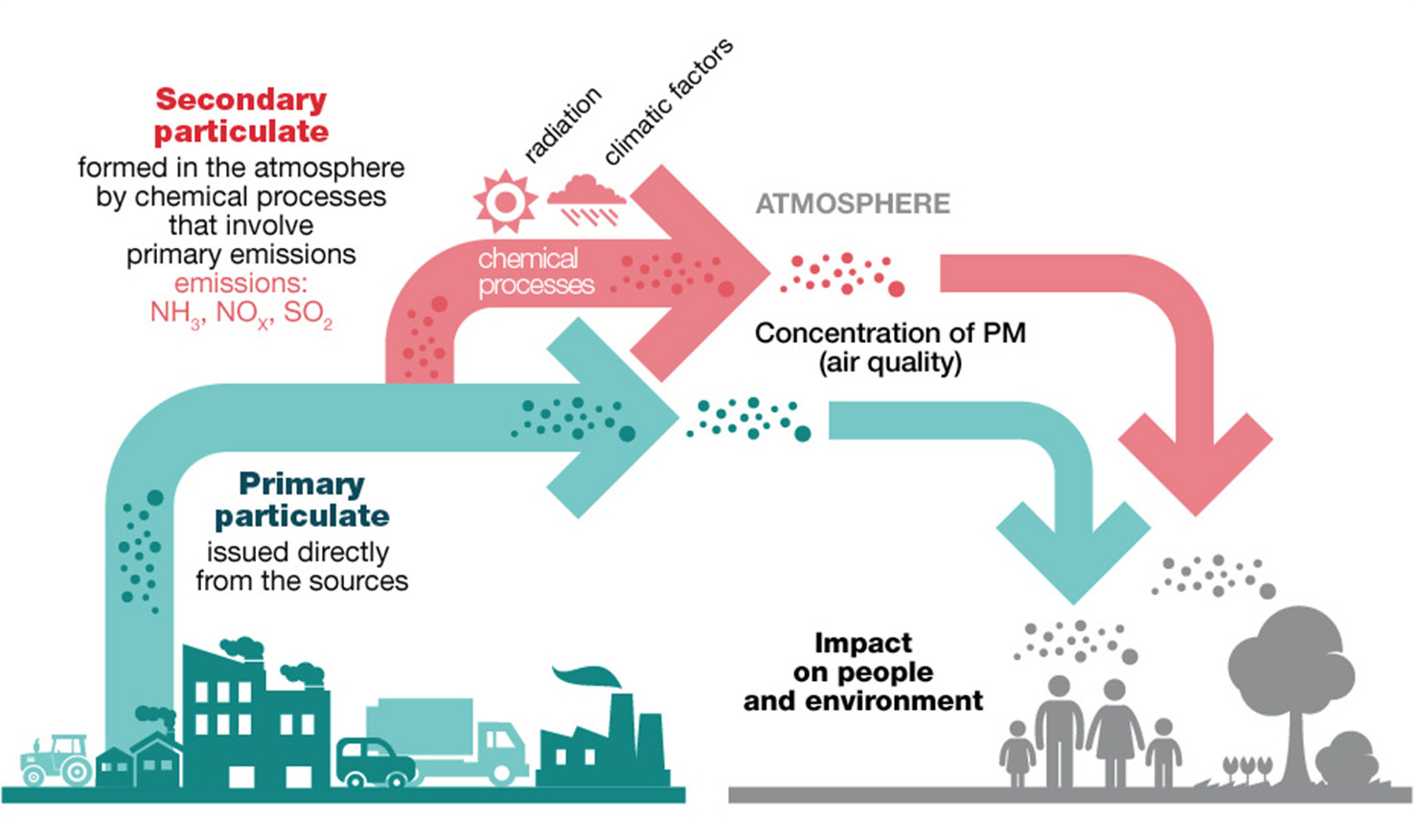
↑ Primary and secondary particulate matter – from the sources to the impact on people and environment
NATURAL SOURCES
The main natural sources of primary particulate matter are volcanic eruptions, fires, the erosion and disintegration of rocks, plants (pollen and vegetal by-products), spores, sea spray and the remains of insects.
On the other hand, secondary natural particulate is constituted by particulate matter originated by the oxidation process of such substances as the nitric oxide released by the ground and the terpene (unsaturated hydrocarbon) emitted by vegetation.
ANTHROPIC SOURCES
Anthropically-originated primary particulate is, again, typically caused by the usage of fossil fuels, the emissions of vehicles, the wearing out of tires, brakes and pavement, alongside with several industrial and farming activities.
↗→ Pollen and volcanic eruptions are natural cources of particulate matter